Autonomy in Space with Machine Learning
Ateleris designed a prototype algorithm in embedded C for the STIX flight software that optimizes the image product quality and telemetry rate requirements autonomously. The poster from the final presentation session at the Swiss Space Office can be viewed online.
Ateleris successfully submitted a proposal to the Swiss Space Center Call for Ideas in 2019 and was selected to design and implement a flight software autonomy algorithm for the STIX instrument. STIX is one of 10 solar instruments onboard the European Space Agency’s Solar Orbiter mission launched in February 2020. Ateleris is a long-term partner of the STIX core team and has been involved in testing, verifying, and maintaining the STIX flight software.
In this study’s frame, the STIX core team and Ateleris designed the so-called Autonomous Interval Selection Algorithm. Ateleris then implemented the algorithm in C and integrated it as a prototype embedded software module into the STIX flight software.
As this optimization algorithm has a machine learning model at its core, it must be trained to be efficient and reliable. Therefore, Ateleris developed an external test harness that could repeatedly run and optimize the algorithm with simulated STIX observation data.
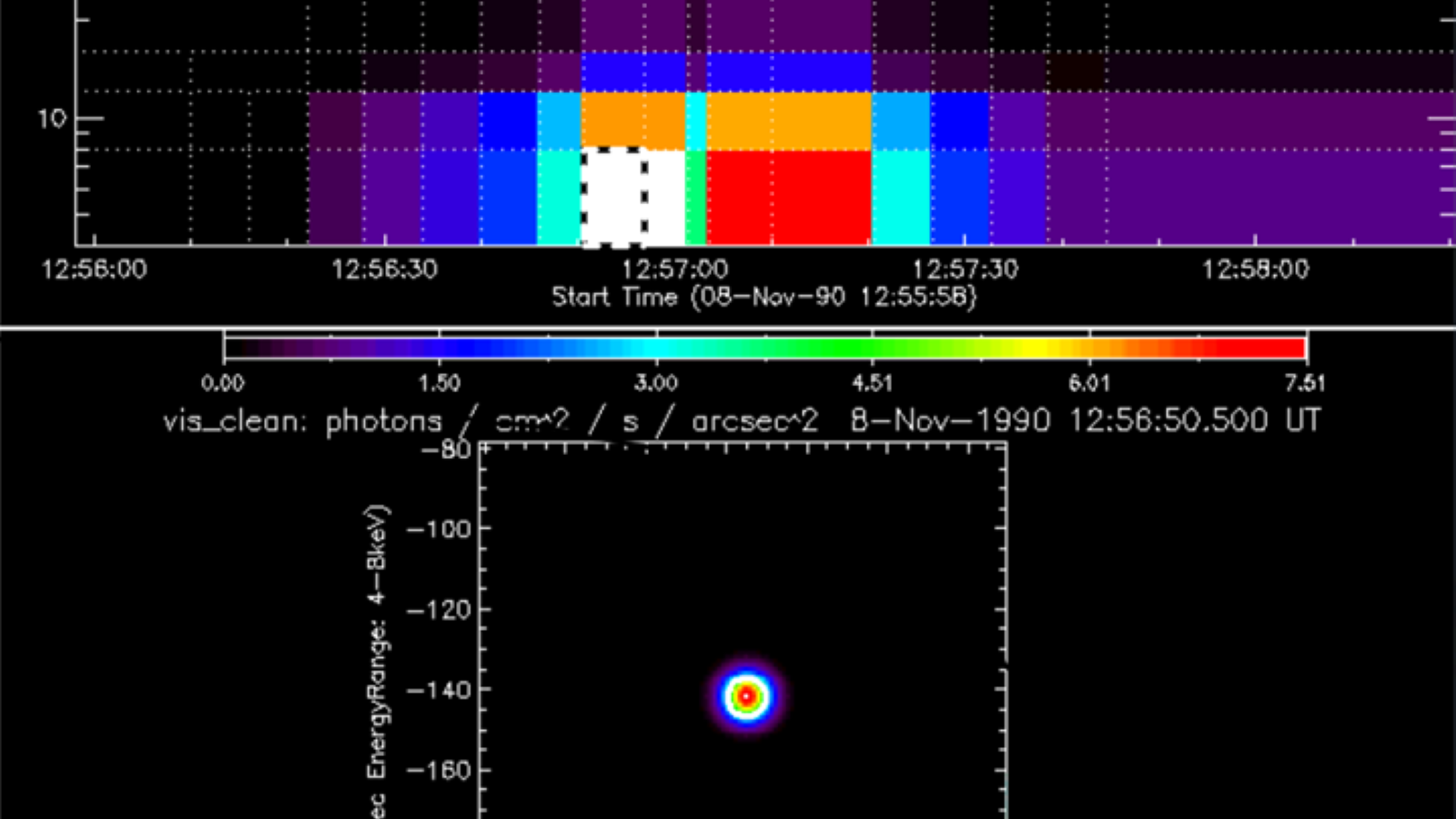
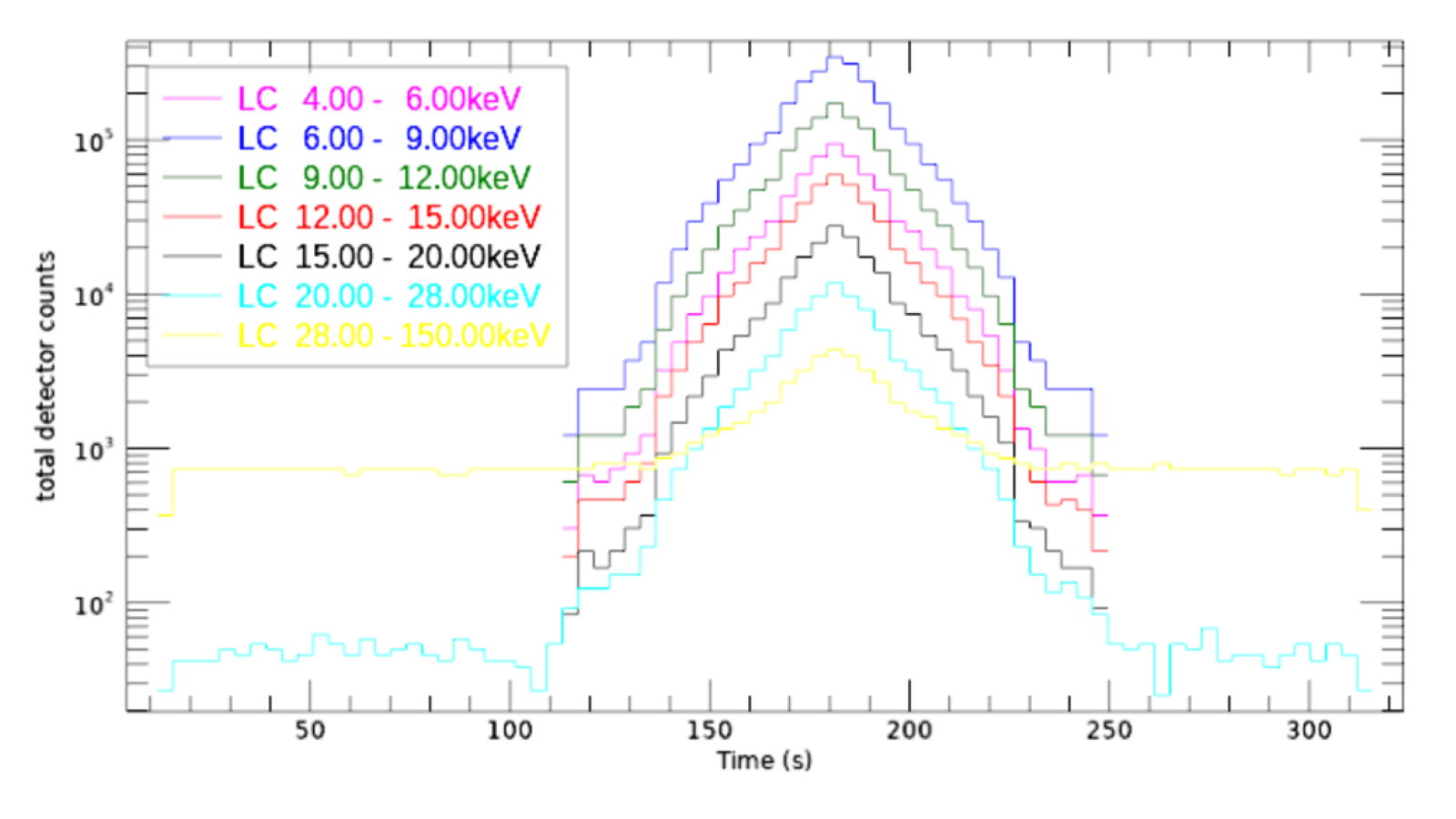
The optimization algorithm runs directly from within the onboard STIX flight software. It autonomously selects and processes an optimal image data cube from the observed data without any user intervention. As a result, the optimization algorithm tremendously improved the image product quality, while at the same time, it reduced the telemetry data rate requirements by a factor of ten.
Key Technologies/Terms
- Embedded software in C/C++
- Machine learning models, parameter search and optimization, autonomy algorithm
- Research and Development
- Space Application